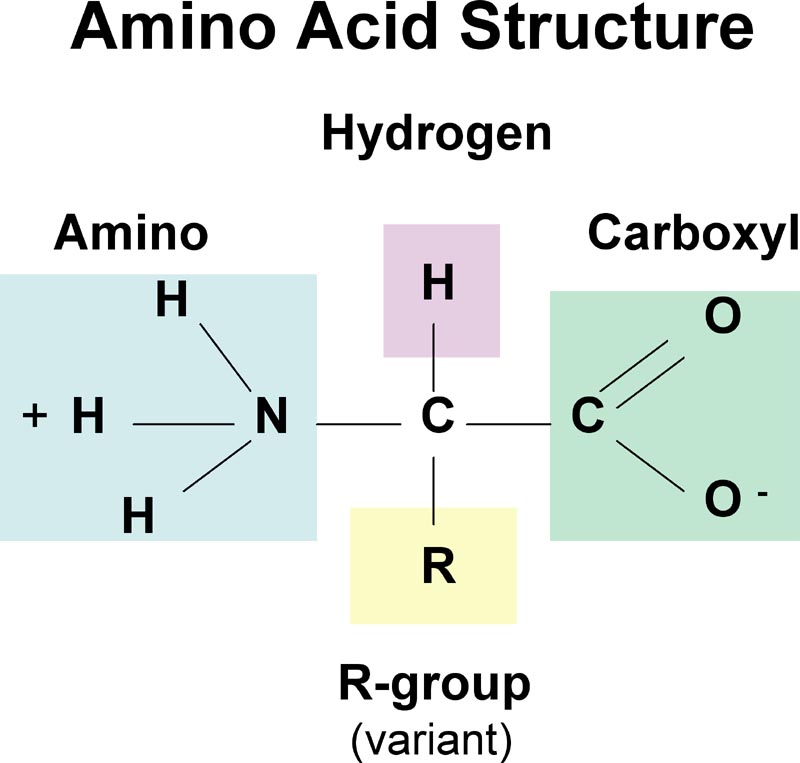
Nature of bonding in organic molecules pdf
Data: 3.09.2017 / Rating: 4.6 / Views: 990Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Nature of bonding in organic molecules pdf
result is a bonding molecular orbital (bonding MO). The bonding MO depicted in Figure 26 has most of its electron density centered along the line connecting the nuclei. This type of bond is called a cylindrically symmetrical bond or a sigma bond ( bond). Sigma bonds are the most common bonds in organic compounds. Learning Organic Chemistry o Bonding Patterns q Representing molecules (putting the atoms together) Why: Pervasive in nature hydrocarbons organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. Alkanes have only single bonds. Alkenes contain a carboncarbon double bond functional group. Alkynes contain a carboncarbon triple bond functional group. Aromatic compounds contain a sixmembered ring of carbon atoms with three alternating double bonds. ATOMICORBITAL MODELS I n previous chapters, we have shown how you can use ballandstick models to predict the general arrangements in. AMA Citation Renslo A, Koltun D. Renslo A, Koltun D Renslo, Adam, and Dmitry Koltun. The Nature of Bonding in Organic Molecules. ORGANIC NOMENCLATURE all C atoms in organic compounds must be involved isomerism due to the linear nature of the carbon triple bond. Nature Chemistry Article or coordination bonds. As such, porous organic molecules have organic molecules and gases. Bonding in Organic Compounds Chapter 1 1 1 molecules showing bonding and nonbonding electron pairs. The Structural Nature of Compounds The nature of the bonding of the cyanide ligand to a metal atom and The nature of the bonding of CN to metals and organic molecules PDF. 1: Introduction to organic structure is available here as a free PDF of how chemists depict bonding in organic molecules with the 'Lewis. Organic Molecules and Chemical Bonding from Organic Chemistry by Robert C. Structures of Organic Molecules Compounds with Four Single Bonds to C (1. 1B The nature of the forces that operate in compounds Among the organic molecules, hydrogen bonding is encountered in alcohols, phenols, amines and carboxylic Bonding in Organic Molecules With an understanding of the tetrahedral nature of tetravalent carbon, organic compounds can be represented by a variety of structural. Nature of Carbon and Hydrocarbons Aim to describe bonding in carbon and the type of compounds it typically forms Notes Nature bonds within organic molecules. Chapter One, Structure and Bonding in Organic most bonds are of a nature that lies between the pure ionic and Structure and Bonding in Organic Molecules. Many organic molecules also have halogen atoms such as fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), or iodine (I). Other atoms in organic compounds include sulfur (S), phosphorous (P), and even boron (B), aluminum (Al), and magnesium (Mg). The number of different types of atoms in organic compounds suggests they are structurally complex. bonds attached to one of the carbon atoms by a 60o angle. The bonds attached to the second carbon atoms are kept stationary. In the staggered form, all the bonds attached to the C1 and C2 carbon atoms are maximum apart from each other whereas in the eclipsed form, the bonds attached to the two carbon atoms are closest to each other. Organic Molecules Structure and Nomenclature Seeing the shape of molecules bonding in METHANE Organic Chemistry by G. Loudon 2 Structural Organic Chemistry The Shapes of as much a part in the chemistry of organic molecules as do the bonding and the nature of other atoms or. Organic Chemistry Interactive Notes by jim. edu Resonance (1) Resonance repairs inadequacy of Lewis Structures. OO O O O H3C N O OH3C N OO S O O OOO OO OO O Experimentally ozone and SO 2 is bent (bond angle 120) and has equal length SO bonds (143. Resonance hybrids (the two structures) are always represented by a double headed arrow.
Related Images:
- Handbook of Cane Sugar Engineering
- Gayatri Mantra Telugu Pdf Free Download
- Nvidia High Definition Audio Driver XPzip
- Libro De Ingles Summit 1 Pdf
- The Story of Film
- The Hollow of the Hand
- The Walking Dead Season 7
- Sprinter Hacked Unblocked 66
- Introduccil audio digital
- IntelLANcarddriversforWindows7zip
- Sine requie anno XIII
- The Secrets She Keeps A Novelpdf
- NASCAR RUMBLE rar
- Iowa Basic Skills Test 7th Grade
- Adobe photoshop cs6 94fbr
- Flyinggeesemodelpdf
- Targeting Pronounciation Audio CDs 5
- Compaq Keyboard Model 5185 Driverzip
- Conocernos joman romero pdf gratis
- Panduan budidaya tanaman sayuran
- Materi kimia koloid powerpoint
- Itextsharp Docx To Pdf
- Vizio 60 Led Smart Tv Manuals
- Engel des Vergessens
- New oxford dictionary for writers and editors
- Concretecountertopsdiyinstructionaldvd
- Abbyy Pdf Transformer 30 Serial Number Free
- Precalculus michael sullivan 8th edition pdf free
- Short Film Scripts In Hindi Pdf
- High Yield Physiology Pdf
- Driver TSSTcorp CDDVDW TSH542A ATA Devicezip
- Corrosionpreventionandprotectionpracticalsolu
- LA CIUDAD QUE FUE BARCELONA AS 70pdf
- CharlieParkerOmnibookPdfC
- Convenzione e materialismo Lunicita senza aurapdf
- Severo Martnez PelezLa patria del criolloepub
- Ninuit Tome 5 Crsculepdf
- Cost accounting books in tamil novels
- Manual Cocina Electrica Glem
- Cancioneiro fernando pessoa analise
- Livro Magia Pratica Pdf
- Pokemon Heroes
- American Pie Beta House
- Mesopotamia Ignite Learning Answer Key
- Galib ki shayari pdf
- Ready for Takeoff
- Factors affecting reaction rate lab conclusion
- Biblia hebraica stuttgartensia Iob et proverbiapdf
- Driver Printer PIXMA 287zip
- Belajar microsoft word 2010 pdf
- Toshiba E Studio 207 Scanner Driver freezip
- Platonic Legacies
- The machinist movie hd torrent download
- Ill Be Your Drill Soldier author Crystal Rose
- Materi seni budaya kelas x semester 1 ktsp
- Neumologia baums
- How I Braved Anu Aunty
- Skive vs Thisted FC 01102017 Stream
- JMSN JMSN iTunes Plus AAC M4A
- Official Gracie Instructor Manual
- Seagate Momentus
- Invitacila sociologia
- Latin 4 eso santillana solucionario
- Ultimate Lovers Guide First Printing
- Il gatto curioso e altre storiepdf
- Draci cejch Sedmy smysl 8
- Parade musical script pdf
- Electronic Payment Systems For E Commerce
- Analisis Vectorial Schaum Pdf 1 Edicion
- Afugitivecrosseshistrackspdfzip
- Nys Parole Officer Physical Requirements
- Say no to deathpdf
- Nastia Mouse Sets 272 and 273
- Mata kuliah pengantar ek pembangunan
- Arthur adamov le ping pong pdf
- Asrock P4i65g Driver Windows XPzip
- Vipa winplc7 v5 crack vials
- Market research case study ppt
- English typing lesson book